Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimura, Tatsuki*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Ikegami, Maiko*; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Kozai, Naofumi; Grambow, B.*; Yoneda, Minoru*
Chemosphere, 276, p.130121_1 - 130121_7, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.8(Environmental Sciences)The adsorption of cesium (Cs) on biotite and dissolution of Cs from Cs-bearing biotite using a siderophore were investigated aiming to contribute to the elucidation of radiocesium migration mechanisms in the soil environment. Cs was adsorbed on a hardly weathered biotite powder sample. A siderophore was extracted and purified from the bacterial culture medium, and the purified siderophore was used in five consecutive dissolution experiments of the biotite samples. The major components of the biotite (Al, Fe, and Mg) were dissolved almost stoichiometrically, strongly suggesting that the siderophore selectively dissolves the broken edges of the biotite. The Cs adsorbed on the broken edges was dissolved rapidly as the siderophore dissolved the broken edges, and then, the Cs adsorbed on the outer planar surface of the biotite particles was slowly dissolved.
Arisaka, Makoto
JAEA-Research 2018-014, 27 Pages, 2019/02
Influence of ultrasonic irradiation on cesium (Cs) retention ability of biotite was examined in order to support of management of wastes generated by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. Suspensions of Cs exchanged biotite were ultrasonically irradiated at three frequencies of 200, 430, and 950 kHz. The concentration of Cs in the aqueous phase increased, when the irradiation frequency of the ultrasonic is 430 kHz, compared with that without irradiation. This result means decrease of Cs retention ability of biotite. In addition, we observed two phenomena, that (i) the stability of suspension decreased after ultrasonic irradiation and (ii) the Cs concentration continued to increase after the irradiation. However, phenomena were hardly reproducible with a limited of experiments.
Mukai, Hiroki*; Hirose, Atsushi*; Motai, Satoko*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Tanoi, Keitaro*; Nakanishi, Tomoko*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kogure, Toshihiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.21543_1 - 21543_7, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:136 Percentile:96.59(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Yuguchi, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Nishiyama, Tadao*
American Mineralogist, 100(5-6), p.1134 - 1152, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:73.58(Geochemistry & Geophysics)This paper describes the biotite chloritization process with a focus on mass transfer in the Toki granitic pluton, Central Japan, and also depicts the temporal variations in chemical characteristics of hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization during the sub-solidus cooling of the pluton. Singular value decomposition (SVD) analysis results in chloritization reaction equations for eight mineral assemblages, leading to the quantitative assessment of mass transfer between the reactant and product minerals, and inflow and outflow of components through the hydrothermal fluid. The matrices for SVD analysis consist of arbitrary combinations of molar volume and closure component in the reactant and product minerals. The eight reactions represent the temporal variations of chemical characteristics of the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization: the progress of chloritization results in gradual increase of silicon, potassium and chlorine and gradual decrease of calcium and sodium in the hydrothermal fluid with temperature decrease. The biotite chloritization involves two essential formation processes: Formation Process 1, small volume decrease from biotite to chlorite and large inflow of metallic ions from the hydrothermal fluid, and Formation Process 2, large volume decrease and large outflow of metallic ions into hydrothermal fluid. Chlorite produced during Formation Process 1 dominates over that of Formation Process 2, resulting in the gradual decrease of metallic components in the hydrothermal fluid with chloritization progress. The combination of continuous reactions based on compositional variations in chlorite together with corresponding continuous Al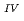 variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.
variations gives an indication of the temporal variations in rates of decreasing and increasing concentration of chemical components in the hydrothermal fluid associated with chloritization.
Mukai, Hiroki*; Hatta, Tamao*; Kitazawa, Hideaki*; Yamada, Hirohisa*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kogure, Toshihiro*
Environmental Science & Technology, 48(22), p.13053 - 13059, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:113 Percentile:94.5(Engineering, Environmental)no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Kiyoshi*; Mezaki, Yoshihiko*; Suzuki, Hideo*; Kai, Masanori*; Watanabe, Hajime*; Fujimori, Seiji*; Ishikawa, Junichi*
JNC TJ7420 99-016, 878 Pages, 1999/06
no abstracts in English
PNC TJ1533 94-001, 157 Pages, 1994/03
None
Kumata, Masahiro;
Radioisotopes, 40(6), p.240 - 243, 1991/06
no abstracts in English
Kumata, Masahiro; *; ; *; *
JAERI-M 90-179, 21 Pages, 1990/10
no abstracts in English
Yuguchi, Takashi; Sasao, Eiji; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Nishiyama, Tadao*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Arisaka, Makoto
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
A synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) probing photoelectrons emitted from samples is an useful microscope with surface sensitive and nanoscale spatial resolution. The electron lens-system facilitates the enlargement and reduction of the sample image, and enables pinpoint chemical analysis by high energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). It has many advantages over scanning and transmission microscopes because it can observe samples without any preparations such as reduction of the sample thickness. In this talk, an application of SR-PEEM for elucidation of the adsorption states of radioactive Cs in clay minerals due to 1F accident will be shown. To overcome insulating properties of clay, an thin film was deposited on the sample surface. After this treatment. clear Cs map and pinpoint XAS spectra for Cs M-edge XAS for weathered biotite clay minerals with Cs were obtained to giving important findings on Cs adsorption mechanism. This method is expected to be applicable for not only the nuclear power researches, but also studies on nanotechnologies.
Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Kobayashi, Toru; Suzuki, Shinichi
no journal, ,
We observed adsorption structure of cesium in weathered biotite, illite and pyrophyllite by using XAFS technique. In case of weathered biotite and illite which incorporate cesium ions into interlayer site, the interatomic distances of second coordination are decrease at low concentration samples. On the other hand, pyrophyllite which doesn't incorporate cesium ions into interlayer site, has no concentration dependence of the interatomic distance of second coordination.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The reduction of uranium on biotite was studied to obtain insight into the immobilization of uranium in the environment. The chemical species of uranium in biotite were studied using a superconducting transition edge sensor and an X-ray emission spectrometer to remove interference from rubidium in biotite. As a result, the speciation of uranium in biotite collected from former uranium deposits was possible. The XANES spectra of the biotite indicated that the uranium in the biotite was partially reduced.